Indicator scoreboardEMU — April seasonally adjusted industrial output sank 0.5 percent and 1.2 percent when compared with last year. Intermediate goods sector fell 0.5 percent and the energy sector dropped 0.7 percent. Durable consumer goods industrial output rose by 1.3 percent, for capital goods by 0.7 percent and for non-durable consumer goods by 0.4 percent. But these categories were down when compared with last year by 6.7 percent, 3.2 percent and 0.6 percent respectively. 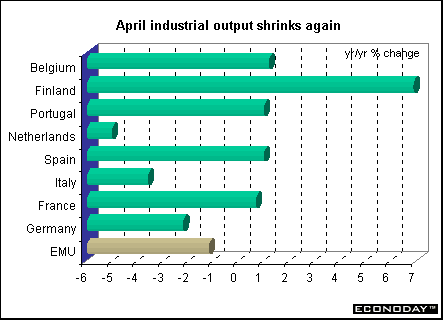
May harmonized index of consumer prices rose 0.1 percent and 2.0 percent on the year. The ECB’s inflation target is 2 percent. Core HICP, which excludes energy, food, alcohol and tobacco, rose 0.3 percent and 2.6 percent on the year. Price increases were recorded for hotel/restaurant services, recreation, household equipment and clothing. Price decreases were recorded for energy and communications. 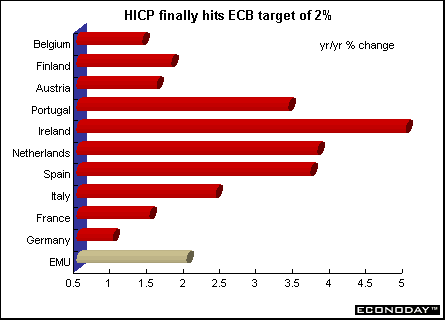 April seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus with the rest of the world was €6.1 billion, down from €9.6 billion in March. Exports slipped 1 percent while imports rose 3 percent. On an unadjusted basis, EMU exports rose 5 percent on the year, while imports rose 1 percent. Germany — May wholesale prices fell 0.4 percent and were down 1.3 percent when compared with last year. Seasonal food prices (fresh fruit and vegetables) fell 7.4 percent and 4.4 percent on the year. Excluding seasonal food prices, wholesale prices fell 0.1 percent and 1.1 percent on the year. Excluding oil products, wholesale prices fell 0.5 percent and 0.8 percent on the year. France — April seasonally adjusted current account surplus widened to €1.226 billion. Merchandise exports jumped 5.0 percent while imports rose only 1.3 percent. The services surplus widened slightly amid declining flows. Imports dropped 7.3 percent, while exports fell 2.8 percent. May seasonally and calendar adjusted consumer spending on manufactured goods dropped 1.3 percent, with a downturn in all sectors except household durables. However, when compared with last year, spending was up 2.0 percent. Spending on manufactured goods accounts for 27 percent of total consumer spending, and erratic monthly results are often revised. Total durables spending was 1.1 percent higher, thanks to a rebound in household durables. Excluding the auto sector and medical products, spending was down 1.3 percent on the month but 1.9 percent higher on the year. Italy — April industrial orders jumped 8.3 percent when compared with last year, the strongest gain since January 2001. Domestic orders rose 4.7 percent while foreign orders surged 13.9 percent. Domestic orders account for around 62 percent of the overall index, with foreign orders making up some 37 percent. Eight of ten product sectors rose. April seasonally adjusted orders (which are not closely followed by most analysts) gained 0.4 percent from March. April domestic orders shed 1.8 percent on the month, while orders from abroad rose 3.6 percent. Britain — May retail price index (RPI) climbed 0.3 percent and 1.1 percent when compared with last year. The retail price index excluding mortgage interest payments (RPIX) increased 0.3 percent and 1.8 percent on the year. The Bank of England, with an inflation target of 2.5 percent, uses the RPIX as its gauge. Lower food and energy costs contributed to the benign rate. 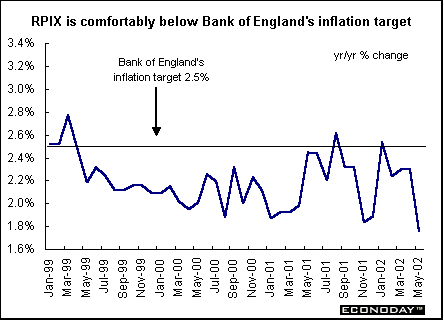 May seasonally adjusted retail sales volumes fell 0.6 percent but were 5.4 percent above levels a year earlier. This was the largest monthly decline since February 2000. National Statistics advised caution when interpreting monthly changes in sales due to problems with the seasonal adjustment. The late May bank holiday was put back a week this year and fell in June and an extra public holiday for the Queen's Golden Jubilee was also added in June. The drop was due largely to falling clothing and footwear sales. In the three months to May, retail sales volumes rose 1.9 percent compared with the previous three months, up from 1.8 percent in the three months to April. 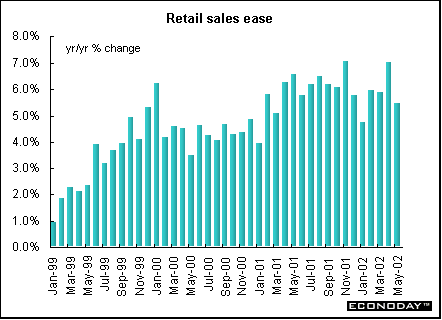 Asia Japan — May seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus widened to ¥908 billion ($7.3 billion) from a revised ¥775.4 billion as exports gained for a fifth straight month. Exports climbed 5.7 percent, the biggest gain since January. Imports rose 3.2 percent. The increase in exports was led by autos, with car shipments to the U.S. and Europe rising by a third from a year ago. Sales of memory chips and electronic parts to Asia rose by a fifth from a year ago, and steel shipments rose 38 percent. By volume, exports gained 15 percent from a year ago, led by a 22 percent increase to Asia. April seasonally adjusted tertiary industry index fell 1.5 percent after a 1.3 percent rise in March. When compared with a year ago, the index fell 1.2 percent. The tertiary index tracks activity at insurers, banks, power utilities and other service providers. Demand at financial institutions and insurance providers fell 1.1 percent in April, and wholesalers, retailers, and restaurants declined 0.6 percent. The all-industry activity index (which adds factory production, government spending and other components to the tertiary index to create a proxy for gross domestic product) fell 1.3 percent from a month earlier. It declined 2.5 percent from a year earlier, the 11th straight decline. Americas Canada — April manufacturers’ shipments jumped 5.0 percent. Even though eighteen of the 21 major groups representing 93.3 percent of total shipments rose, the major impetus came from the motor vehicle sector. Excluding that industry, April's shipments rose 3.3 percent. Unfilled orders rose 0.6 percent, a third consecutive monthly increase. Excluding the effect of the aerospace product and parts industry, unfilled orders grew by 2.1 percent. New orders grew 4.5 percent, the highest level since May 2001. April merchandise trade surplus jumped 11.0 percent to C$5.2 billion, the highest level since May 2001. Merchandise exports rose 2.9 percent to C$34.3 billion, the highest level since June 2001. Export growth was particularly strong in automotive products, which rose 4.1 percent. Machinery and equipment increased 2.6 percent. Merchandise imports rose 1.6 percent to C$29.1 billion. The trade surplus with the United States jumped 8.2 percent. Canadian exports to the United States jumped 2.4 percent while imports eked up 0.3 percent. Canada's total trade deficit with nations other than the United States rose C$109 million to C$3.1 billion in April. 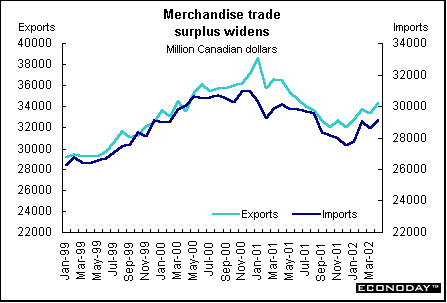 April retail sales rose 1.0 percent after remaining essentially flat in March. In constant dollars, retail sales rose 0.3 percent. Gasoline and cigarettes posted the most significant price increases. All retail sectors posted higher sales except in drug stores. Retailers in the clothing, furniture and general merchandise sectors enjoyed the largest sales increases. 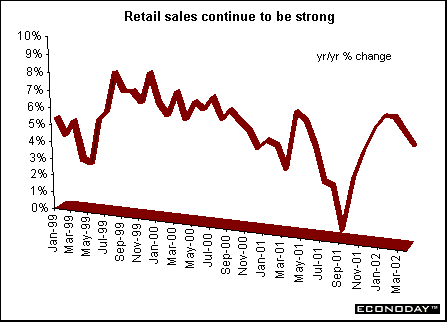 |