
Indicator scoreboard
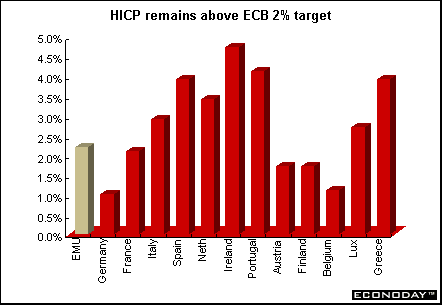
EMU - November harmonized index of consumer prices fell 0.1 percent but rose 2.2 percent when compared with last year. Core HICP - excluding energy, food, alcohol and tobacco prices - rose 0.1 percent and 2.3 percent on the year. HICP excluding energy and unprocessed foods - the core inflation measure favored by the ECB - also rose 0.1 percent and 2.3 percent on the year. Eight of the 12 countries reported annual inflation rates above the ECB's 2 percent price stability ceiling. Of those eight, two were above 4 percent and another three were above 3 percent.
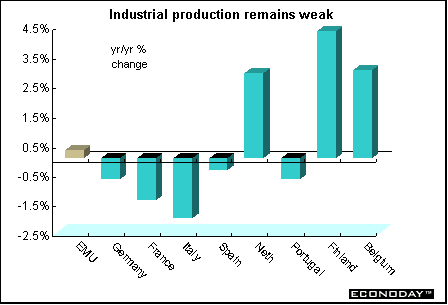
October seasonally adjusted industrial output fell 0.2 percent but rose 0.3 percent when compared with last year. September industrial production was revised to unchanged from a decline of 0.2 percent and to a decline of 0.3 percent from the originally reported decline of 0.6 percent on the year. Output declined in all sectors but capital goods.
October merchandise trade surplus was €8.7 billion, a sharp drop from the €10.1 billion surplus a year earlier. Exports were unchanged on the year while imports rose 2 percent. The seasonally adjusted trade surplus at €6.8 billion was sharply below the September surplus of €10.2. Exports fell 3 percent while imports rose 1 percent from the preceding month.
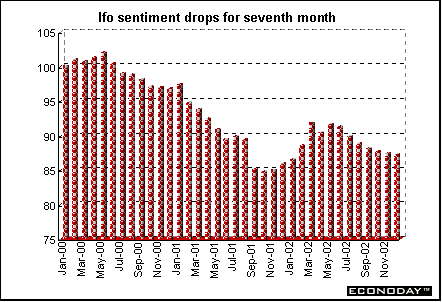
Germany - December Ifo Institute's west German business sentiment index fell to 87.1 from 87.3 in November, its lowest level since January. The current conditions sub-index fell to 76.8 from 79.0 while business expectations sub-index rose to 97.9 from 95.8 in November.
November seasonally adjusted producer prices fell 0.1 but rose 0.5 percent when compared with last year. Nonseasonally adjusted prices fell 0.2 percent but rose 0.4 percent on the year. The decline was due to a significant drop in energy prices. Excluding energy prices, the PPI was unchanged on the month and up 0.6 percent on the year.
October seasonally adjusted industrial production was revised to a minus 1.3 percent decline from the originally reported drop of 2.1 percent. Industrial production excluding construction - the figure that is used to calculate eurozone industrial output - was revised up to a decline of 1.4 percent from the originally reported 2.1 percent drop. Manufacturing output was revised to a decline of 1.7 percent from the originally reported 2.1 percent fall.
France - October seasonally adjusted current account surplus fell sharply to €163 million, as a drop in the services surplus outweighed an upturn in the trade surplus. The merchandise trade surplus recovered to €865 million from €207 million, as imports plunged 7 percent while exports fell 4.5 percent. The services surplus, by contrast, narrowed sharply to €1.288 billion from €2.309 billion, with revenues down 8.4 percent while outlays rose 6.3 percent.
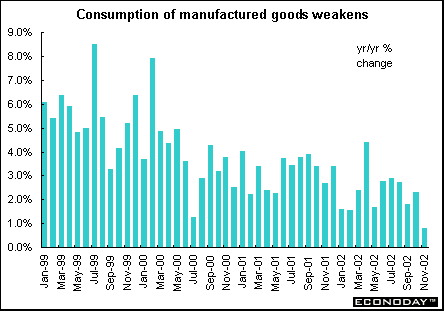
November seasonally and calendar adjusted consumer spending on manufactured goods fell 1.7 percent, more than erasing October's rebound on broad-based declines led by textiles. However, spending is up 0.8 percent on the year. The declines were led by the volatile textile and leather goods component, which plunged 9.6 percent on the month and was off 7.9 percent on the year. Sales of other manufactured goods, including cosmetics, drugs, car parts, jewelry, photo and sporting goods, were also down 0.7 percent on the month. Auto sales fell both on the month and on the year. Spending excluding the auto sector and medical products also fell on the month. Household durable spending, by contrast, remained robust, with a 3.7 percent jump on the month and a 13.4 percent gain on the year.
Italy - October seasonally and workday adjusted industrial production sank 0.9 percent and 2.0 percent when compared with last year. A strike by Italy's largest trade union, the CGIL, coupled with the crisis at car-maker FIAT, weighed on October's output.
November merchandise trade balance with non-EU countries fell to a surplus of €1.710 billion when compared with last November's surplus of €2.276 billion. Non-EU exports dropped 1.5 percent while imports rose by 4.5 percent on the year.
October industrial orders declined 1.2 percent when compared with last year. Domestic orders sank 3.7 percent while foreign orders rose 2.9 percent. Domestic orders account for around 62 percent of the overall index, with foreign orders making up the rest. Seasonally adjusted orders data, which are not closely followed by most analysts, fell 3.7 percent on the month. Domestic orders plummeted 4.5 percent while overseas orders fell 2.7 percent.
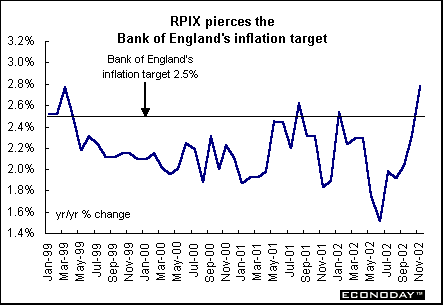
Britain - November retail price index rose 0.2 percent and 2.6 percent when compared with last year. The retail price index excluding mortgage interest payments also rose 0.2 percent but jumped 2.8 percent on the year. The RPIX, which is the Bank of England's inflation measure, was above the Bank's target rate of inflation of 2.5 percent. The RPIX was boosted by rising gasoline and house prices. The annual rate was the highest since June 1998.
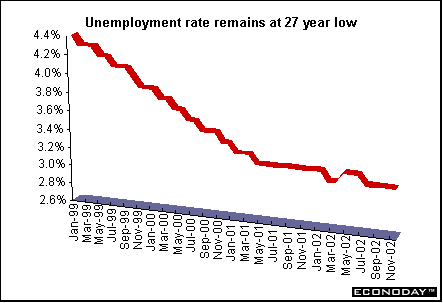
November claimant count unemployment fell 6,200 to 934,200, its lowest level since 1975. However, unemployment for the three months ending in October rose 19,000 on the International Labour Organization measure (excluding jobseekers who did any work during the month). The November claimant count unemployment rate was 3.1 percent. The ILO unemployment rate for the three months ending in October remained at 5.2 percent.
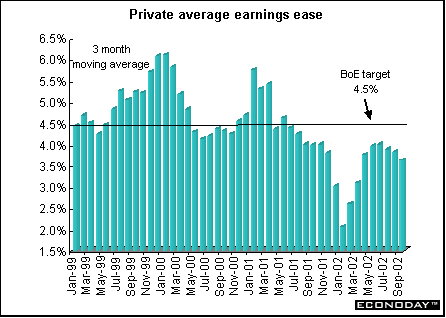
October average earnings rose 3.7 percent, down from 3.8 percent in September. However, public sector earnings growth continued to pick up, rising from 3.6 percent in September to 3.8 percent in October. This was the first time since April 2002 that public-sector growth exceeded private-sector growth, which stood at 3.6 percent. Pay excluding bonuses rose 3.8 percent on the year to October.
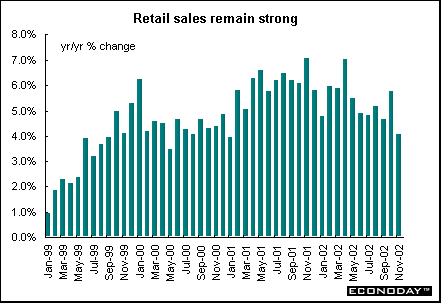
November retail sales volume rose 0.1 percent and was up 4.0 percent when compared with last year. Large retail stores performed strongly but overall clothing and footwear sales declined sharply. Food store sales were up while non-food store sales fell.
Third quarter business investment was revised up to show a drop of 2.2 percent on the quarter, compared with the preliminary estimate of a 2.8 percent decline. On the year, business investment sank 9.8 percent. Service sector investment fell 2.4 percent on the quarter and 10.7 percent on the year. Construction and other production investment rose 1.5 percent on the quarter but were down 5.2 percent on the year.
Asia
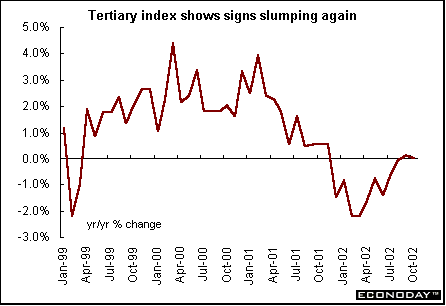
Japan - October tertiary industry index, a gauge of strength in the service sector, fell 0.2 percent, the second straight decline after September's 0.3 percent fall. The tertiary index reflects activity in six industries: utilities, transport and telecommunications, wholesale and retail, finance and insurance, real estate and services. The all industry index fell 0.3 percent. The index takes a reading of activity in the six industries that comprise the tertiary index combined with activity in the construction, agricultural and fisheries industries, the public sector and industrial output. This index is considered a close approximation for gross domestic product growth as measured by industrial and service sector output.
Americas
Canada - October manufacturers' shipments edged up 0.1 percent and were at the highest level since May 2001. Manufacturers boosted shipments of non-durable goods 0.4 percent, the highest level since January 2001. Output of durable goods, which includes big-ticket products such as airplanes, machinery and computers, remained relatively stable. Eleven of the 21 major manufacturing industries, representing 68 percent of total shipments, posted increases. Unfilled orders declined 0.5 percent following a 1.1 percent drop in September. Fewer orders for machinery, aerospace products and parts and heavy trucks offset a rise in unfilled orders for computers and electronic products. New orders posted a 0.8 percent increase, partly recovering September's losses. Manufacturers reported higher orders for computers and electronic products, which offset a sharp decline in the machinery industry.
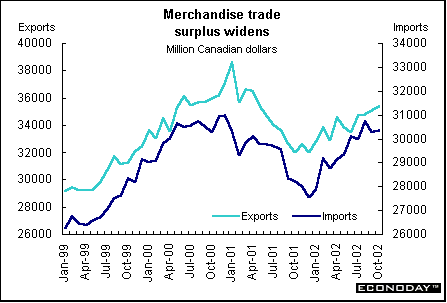
October merchandise trade surplus jumped to C$5.1 billion as merchandise exports rose 0.9 percent to C$35.4 billion and imports inched up 0.3 percent to C$30.4 billion. Canadian companies sent C$30.0 billion in goods to the United States, a slight decline from September. Imports from south of the border increased only slightly to C$21.5 billion. The trade surplus with the United States fell to C$8.4 billion. Canada's trade deficit with countries other than the United States improved from C$3.7 billion in September to C$3.3 billion in October.
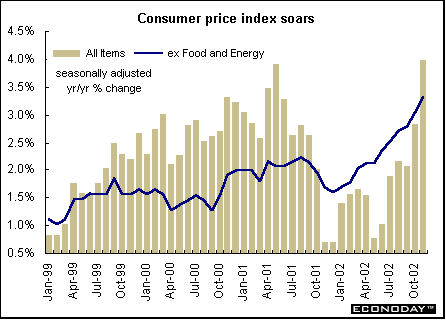
November seasonally adjusted consumer prices rose 0.5 percent and 4.0 percent when compared with last year. Excluding energy and food, the CPI jumped 0.4 percent and 3.3 percent on the year. Upward price pressures came from higher prices for automotive vehicles and fresh vegetables, as well as higher auto insurance premiums and prices for bakery products.


Last Week's Highlights • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
| ![[IP Archive]](../images/iparchive.gif)