
Indicator scoreboard
EMU - Second quarter real gross domestic product was revised to a 0.4 percent gain from the 0.3 percent gain previously reported. On the year, second quarter GDP was revised to 0.7 percent from 0.6 percent. Gross fixed capital formation and net exports were both revised up, while private consumption was revised down.
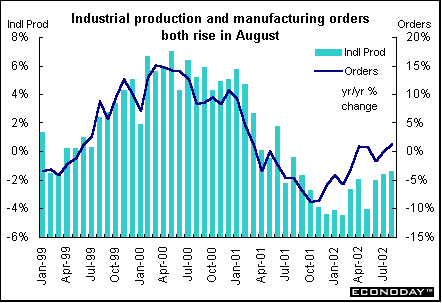
Germany - August manufacturing orders jumped 1.7 percent. They climbed 0.4 percent in west Germany but soared 20.1 percent in the east. The jump in the east was due largely to a huge jump in east German capital goods demand, which surged 44.5 percent on the month. Domestic demand jumped 23.5 percent and foreign orders were up a whopping 82.1 percent. The rise in overall capital goods orders was not related to the rebuilding from floods that hit eastern Germany in August. Rather demand, particularly foreign demand, was heavily influenced by two very large aerospace orders. In west Germany, foreign demand rose 0.7 percent while domestic demand inched up 0.1 percent. Capital goods orders rose 1.9 percent but both consumer and basic goods demand declined.
August seasonally adjusted industrial production rebounded strongly, rising 1.8 percent after a 0.6 percent drop in July. However, industrial production is still down by 1.4 percent when compared with last year. Excluding construction, industry output was up 2.1 percent but down 0.6 percent on the year. Output rose with the exception of consumer durables and construction. Manufacturing output rose 2.1 percent, reversing the 0.6 percent drop in July. Manufacturing output was up in all sub-sectors except in the consumer durables category. In west Germany, industrial output rose 1.5 percent after falling 0.5 percent in July, while in the east, production jumped 5.0 percent after falling 3.3 percent in July.
August seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus stood at €12.6 billion, up from a €10.4 billion surplus in July and a €10.2 billion surplus in August 2001. Exports were up 10.8 percent and up 4.2 percent on the year. Imports were up 8.2 percent but unchanged on the year.
France - August seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus fell to €1.588. Exports fell 4.8 percent primarily due to declining military exports. A decline in exports of pharmaceutical goods and machines was offset by continued strength of automotive exports and strong aeronautics exports. Imports dipped 2.4 percent due a decline of agricultural products and capital goods, while imports for pharmaceutical goods, cars and car-parts rose.
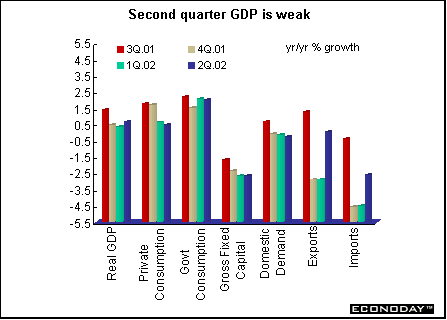
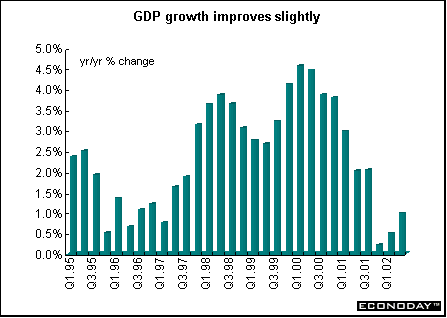
Second quarter seasonally adjusted gross domestic product growth was revised down to 0.4 percent from the previously estimated 0.5 percent. When compared with last year, GDP was up 1.0 percent. Weaker increases in exports and private consumption were responsible for the downward revision.
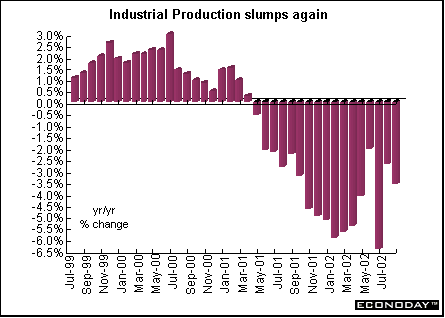
Britain - August industrial production fell 0.3 percent and was down 3.5 percent on the year. Manufacturing output was flat and was down 3.7 percent when compared with last year. Output fell in 12 out of the 13 manufacturing sub-sectors with only an increase in transport output. Significant declines were incurred in electrical and optical equipment, particularly in computers, in basic metals and metal products, and machinery and equipment. Excluding car production, output would have declined 0.7 percent on the month. Industrial output was depressed by an 0.8 percent monthly drop in utilities output and a 2.6 percent drop in mining and quarrying output.
August global merchandise trade deficit widened to Stg2.811 billion from Stg2.405 billion in July. The value of global goods exports fell 8.8 percent in spite of a record increase in car exports, while imports were down 5.5 percent. The volume of exports fell 9.1 percent while imports dropped 5.1 percent. A bigger trade gap with EU countries was the main reason behind this month's deterioration. The goods deficit with EU countries widened to Stg859 million in August from Stg469 million July - the largest shortfall since April 1999. Excluding oil and erratic items the underlying global goods deficit also deteriorated, growing to Stg2.943 billion in August from Stg2.372 billion in July.
Asia
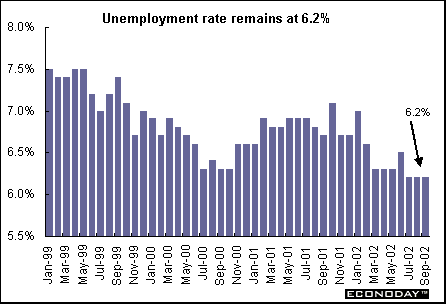
Australia - September seasonally adjusted unemployment rate was unchanged at 6.2 percent but employment shed 30,700 jobs. The worst drought in 100 years has cost the farming industry 40,000 jobs. The drop in employment followed August's rise of 88,500 jobs, which was the biggest increase in 11 years. The economy added 11,700 full-time jobs but lost 42,400 part-time positions. The participation rate, which measures the number of the people with jobs or looking for work, fell to 63.5 percent from 63.8 percent in August.
Japan - September domestic wholesale price index was unchanged and down 0.9 percent when compared with last year. The data show that wholesale prices have fallen for the 24th consecutive month.
August machinery orders fell 13.6 percent - the biggest drop in five years - as slowing exports discouraged manufacturers from investing in equipment to make computer chips and other goods. Machinery orders are at the lowest level in 15 years. The drop in orders, an early indicator of business investment, was the first in five months. From a year earlier, machinery orders fell 20.3 percent after falling 5.8 percent in July. Power utilities and shippers are excluded because their large projects skew the figures. Machinery orders account for about two-thirds of business spending. Capital spending accounts for about 16 percent of the economy.
August seasonally adjusted current account surplus shrank to ¥1.16 trillion ($9.4 billion). The surplus, the broadest measure of trade because it includes investment and services, fell 8.3 percent. The current account surplus widened 49 percent when compared with last year. Exports fell for a third month. Japan's income account surplus, which tracks profits, dividends and interest payments, fell to ¥715.1 billion from ¥791.8 billion in July. The services deficit, which includes overseas travel, rose to ¥340.3 billion from ¥444.6 billion deficit in July.
Americas
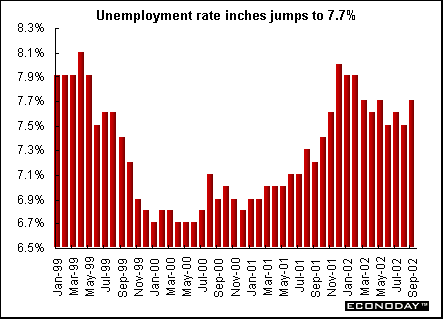
Canada - September employment rose by 41,000 but the unemployment rate rose to 7.7 percent as more persons entered the labor market. The participation rate continued to climb, up 0.2 percent to 67.2 percent, the highest rate in more than 12 years. September's increase occurred mainly in the province of Ontario and three-fourths of it, 30,000, was in transportation and warehousing. Almost half of the 41,000 overall employment gain was among self-employed workers and was concentrated in Ontario.


Last Week's Highlights • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
| ![[Back To Archive]](../../../images/backtoarchive.gif)