
Indicator scoreboard
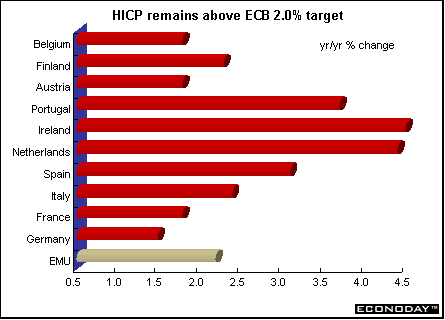
EMU - August harmonized index of consumer prices rose 0.1 percent and 2.2 percent when compared with last year. The rise was due mainly to increased price levels in the services and energy sectors.
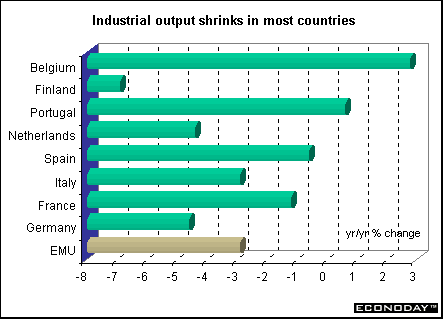
July seasonally adjusted industrial output sank 0.9 percent and 0.5 percent when compared with last year. Output fell in all sectors, led by intermediate goods and followed by non-durable consumer goods, energy, and capital goods and durable consumer goods.
July unadjusted merchandise trade surplus with the rest of the world rose to ?12.0 billion from ?11.0 billion in June. It was also higher than the surplus of ?8.7 billion posted a year earlier. Exports fell an unadjusted 1.0 percent while imports dropped 5 percent from July 2001. On a seasonally adjusted basis, the trade surplus was ?6.5 billion, down from ?7.8 billion in June. Seasonally adjusted exports fell 2 percent while imports fell 1 percent.
Germany -August wholesale prices remained unchanged and were down 0.5 percent when compared with last year. Excluding seasonal food prices, wholesale prices fell 0.1 percent but sank 0.6 percent on the year. Energy prices rose 0.8 in August but were down 1.4 percent on the year. Excluding oil products, wholesale prices fell 0.1 percent and 0.4 percent on the year.
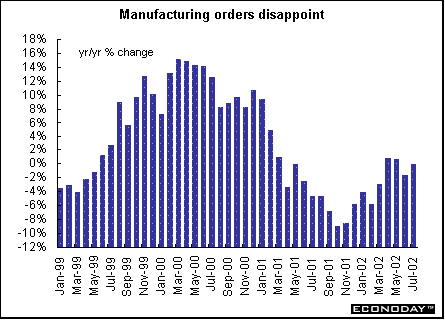
July seasonally and workday adjusted manufacturing orders were revised upward to a decline of 0.4 percent from the 0.9 percent decline originally reported. Foreign orders were revised up to a drop of 1.5 percent from the originally reported 2.0 percent drop, while domestic orders were revised up to a 0.4 percent increase from the unchanged reading originally reported.
France - July seasonally and workday adjusted manufacturing output dropped 1.0 percent to the lowest level since January. Insee, the French statistical agency said that the data should be interpreted with caution. This is the first time that manufacturing output has been calculated for July alone, since results for July-August have traditionally been given as a single period. All manufacturing sectors posted declines, led by consumer goods and autos.
Italy - July seasonally and workday adjusted industrial production climbed 0.6 percent but is down 2.6 percent when compared with last year. Consumer goods' output fell 1.1 percent but output of investment goods climbed 2.2 percent, while intermediate goods rose 0.9 percent.
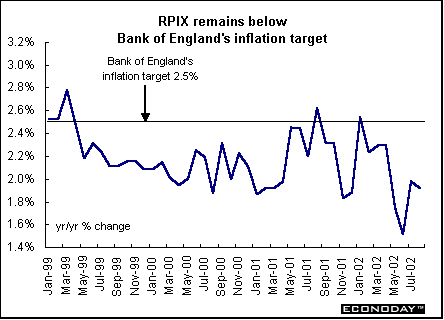
Britain - August retail price index (RPI) rose 0.3 percent and 1.4 percent when compared with last year. The retail price index excluding mortgage interest payments (RPIX) also rose 0.3 percent but was up 1.9 percent on the year. The RPIX remains substantially below the Bank of England's target inflation rate of 2.5 percent.
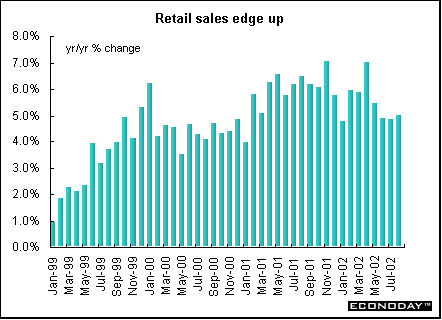
August retail sales volumes rose 0.6 percent and 5.0 percent when compared with last year. Both June and July were revised upward from initial estimates. All sectors rose on the month with household goods spending jumping 1.6 percent, followed by a 1.4 percent rise in non-specialized store sales, a 1.0 percent gain in non-store retailing and repair, and a 0.3 percent increase in textile, clothing and footwear and other store sales.
Americas
Canada - July manufacturing shipments rose 1.0 percent fuelled by strong output of motor vehicles and petroleum and coal products. Following declines in May and June, shipments recovered to the highest level since April. Fourteen of 21 industries reported higher shipments, representing 74 percent of the total. Inventories rose 0.6 percent, the third increase in four months. However, finished-product inventories, which have been trending down since summer 2001, declined a further 0.9 percent. Unfilled orders declined by 0.9 percent for the first drop since April. New orders fell 0.5 percent.
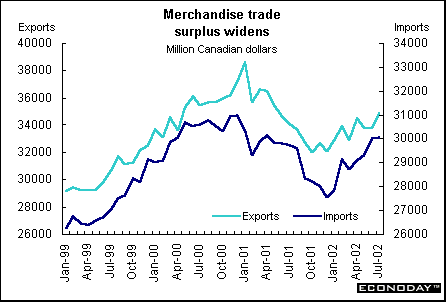
July merchandise trade surplus rebounded to C$4.9 billion from a revised C$3.8 billion in June. Exports jumped 3.4 percent to the highest level since May 2001, in the wake of growth in all principal commodity groups. The entire gain in exports came as a result of a 4.2 percent increase to the United States. Imports crept up 0.2 percent, the fourth straight monthly gain. Canadian companies sent C$29.7 billion in goods to the United States, accounting for 85 percent of total exports. Imports from the United States rose 1.6 percent to C$21.5 billion. Consequently, the trade surplus with the United States reached C$8.2 billion. Canada's trade deficit with other countries narrowed as a result of lower imports from Japan, European Union countries and other countries of the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development.
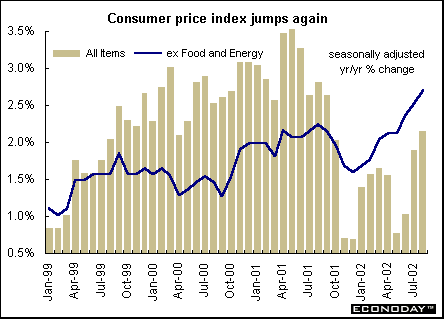
August consumer price index rose 0.4 percent and 2.6 percent when compared with last year. The increase was attributable mainly to the rise in prices for electricity and gasoline, as well as to higher automotive vehicle insurance premiums. August seasonally adjusted CPI rose 0.4 percent and 2.1 percent on the year. Core CPI, excluding food and energy rose 0.3 percent and 2.7 percent on the year.


Last Week's Highlights • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
| ![[Back To Archive]](../../../images/backtoarchive.gif)