
Indicator scoreboard
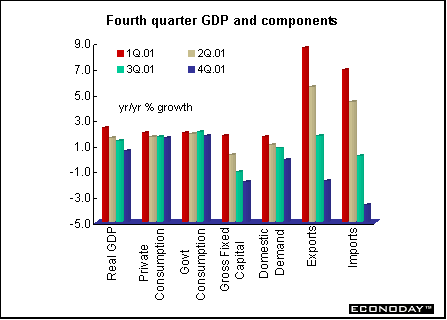
EMU - Fourth quarter real gross domestic product fell 0.2 percent and was up 0.6 percent when compared with last year. The decline was due to weaker investment and a further reduction in inventories. Private consumption edged up 0.1 percent on the quarter and government consumption rose 0.5 percent. But gross fixed capital formation declined 0.8 percent. Inventories dropped 0.4 percent. Domestic demand, the sum of the above categories, fell 0.2 percent on the quarter.
Germany - January seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus was E11.5 billion on a nominal basis, up from an E10.8 billion surplus in December and up from an E7.0 billion surplus in January 2001. German exports adjusted for seasonal variations but not for price differences, dropped 1.7 percent and 3.0 percent on the year. Imports were down 4.0 percent and down 13.0 percent on the year.
February unadjusted final harmonized index of consumer prices was up 0.2 percent and 1.8 percent when compared with last year. The national CPI rose 0.3 percent and 1.7 percent on the year. Excluding heating oil and motor fuels, national CPI rose 0.2 percent and 2.1 percent on the year. Seasonally adjusted consumer prices remained unchanged on the month but were up 1.7 percent on the year.
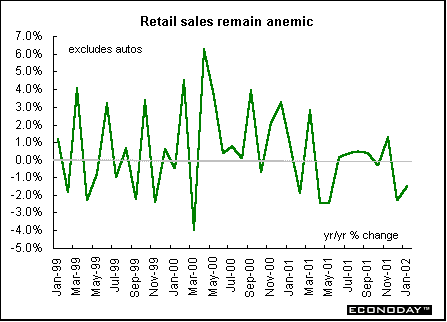
January real seasonally and calendar adjusted retail sales (excluding auto dealerships, gasoline stations and wholesale warehouses) rose 1.4 percent but fell 1.8 percent when compared with last year. Total seasonally adjusted real retail sales (including auto/gasoline station sales) rose 1.2 percent but fell 1.5 percent on the year.
February wholesale price index rose 0.2 percent but fell 0.5 percent when compared with last year. Agriculture product prices rose 0.6 percent and capital goods prices were up 0.5 percent. Excluding seasonal food prices, wholesale prices rose 0.2 percent but fell 1.1 percent on the year. Excluding oil products, wholesale prices rose 0.1 percent and 0.6 percent on the year.
France - February seasonally adjusted consumer price index was unchanged for the month but rose 2.2 percent when compared with last year. The core CPI was also unchanged on the month and up 2.2 percent on the year. The harmonized index of consumer prices rose 0.2 percent and 2.3 percent on the year.
Fourth quarter non-farm payrolls rose 0.3 percent and were 1.5 percent higher than a year ago. The number of jobs added was 51,200. Service jobs rose 0.6 percent. Gains were led by the retail sector, where the euro changeover boosted temporary hiring. Industry jobs dropped by 0.3 percent.
January seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus widened to E1.305 billion. This compares with a trade surplus in January 2001 of E2.773 billion. Seasonally adjusted exports rose 6.6 percent with gains in most sectors except autos. The export upturn was due mainly to flows outside the European Union, particularly to the United States. Imports rose 3.0 percent after more than a year of decline. Gains were strongest in consumer goods and auto parts.
January seasonally and workday adjusted manufacturing output rose 0.9 percent but was down 2.3 percent when compared with last year. This was the first increase in four months. Industrial output excluding construction rose 0.6 percent but was down 1.3 percent on the year. All manufacturing sectors posted an upturn led by consumer goods, which were up 1.4 percent, and semi-finished goods, up 1.2 percent. Capital goods output growth remained weak, up 0.3 percent.
Italy - January seasonally and workday adjusted industrial production rose 0.2 percent but was down 3.4 percent when compared with last year. Output was up on an increase in energy production to meet an unusually cold January. Consumer goods output was down 0.7 percent, investment goods slipped 0.1 percent while intermediate goods rose 1.0 percent.
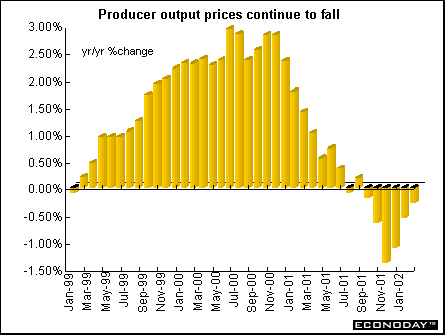
Britain - February seasonally adjusted producer input prices rose 0.2 percent but fell 7.3 percent when compared with last year. Crude oil prices jumped 3.3 percent but were down 25.8 percent on the year. Producer output prices rose 0.1 percent and were down 0.3 percent on the year. Seasonally adjusted core output prices, which excludes food, beverages, tobacco and petroleum, were unchanged and up 0.1 percent on the year.
January merchandise trade deficit fell to Stg2.592 billion from Stg3.140 billion in December. The total trade gap narrowed to Stg1.563 billion from Stg2.061 billion, in spite of a decline in the services surplus, which was Stg1.029 billion, down from Stg1.079 billion in December. The improvement was due to a 4.1 percent increase in global goods exports. This increase more than offset the 0.3 percent climb in imports. Goods exports to non-EU countries rose 12.9 percent while imports rose just 0.3 percent. Exports to the EU fell 2.2 percent while imports rose 0.2 percent. Excluding oil and erratics, the global goods trade narrowed to Stg2.865 billion from Stg3.155 billion in December.
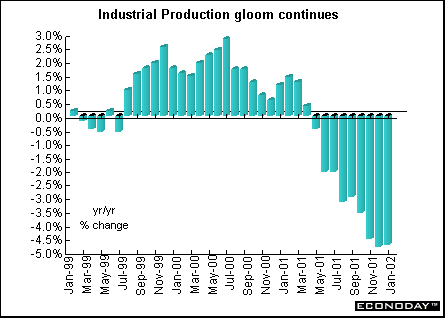
January manufacturing output fell 0.4 percent and was 6.1 percent lower than last year. The decline was almost entirely due to a drop in electrical and optical equipment industries output. Excluding this sector, manufacturing output was up 0.6 percent on the month. The level of manufacturing output is at its lowest since July 1994. Industrial production fell 0.5 percent and 5.2 percent on the year.
Asia
Japan - January machinery orders fell 15.6 percent, the largest drop in nearly 15 years. Core private machine orders were down 22.2 percent from the previous year, signaling that Japan's industrial sector remains mired in a slump.
January seasonally adjusted current account surplus, the broadest measure of trade because it includes income from investment and services, rose to 1.24 trillion yen ($9.6 billion) from a revised 1.02 trillion yen in December. Exports, which accounts for 10 percent of the economy, rose 5 percent while imports rose 3.5 percent. The merchandise trade surplus rose to 844.6 billion yen from 761.0 billion yen in December. The income account surplus, which tracks dividends and interest payments, rose to 798.3 billion yen from a revised 727.7 billion yen in January as companies brought home more profits and investments from overseas. The weaker yen inflates the value of overseas earnings when converted to yen. The services deficit, which includes overseas travel, expanded to 417.7 billion yen in January from a revised 386.5 billion yen in December as people resumed international travel after cutting back in the months following the terrorist attacks on the United States. From a year earlier, the current account surplus widened to 709.0 billion yen from 218.6 billion, unadjusted. Exports fell 2.9 percent while imports fell 11 percent, swelling the trade surplus to 336.8 billion yen from 64.2 billion yen a year earlier.
February bankruptcies totaled 1,674 companies, up 14.6 percent from a year ago. This was the sixth month that the number of bankruptcies increased as banks clear trillions of yen of bad loans from their books by shutting off deadbeat borrowers. Tokyo Shoko Research Ltd. said that the failed companies owed 1.25 trillion yen ($9.67 billion). Tokyo Shoko and Teikoku Data Bank, which also track corporate failures, have forecast that bankruptcies this year will top last year's 17-year high of 19,164.
January industrial output dropped a revised 1.5 percent compared with the initially reported drop of 1.0 percent. Inventories fell a revised 1.5 percent versus a 1.1 percent drop in the initial figures. Production capacity, before adjustment for seasonal factors, fell 1.4 percent during January, the largest rate on record. Unadjusted capacity plummeted 4.1 percent from a year earlier, also the largest rate on record. Electrical machinery manufacturers chopped 3.9 percent of their capacity from December, the most by any industry. Transportation machinery manufacturers followed with a 0.9 percent cut to capacity on the month. The index for production capacity stood at 94.5, the lowest since December 1988 when it was the equivalent of 93.9. The operating ratio for January, after adjustment for seasonal factors, rose 0.8 percent from December.
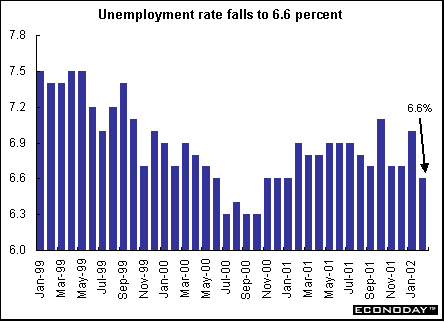
Australia - February seasonally adjusted unemployment rate fell to 6.6 percent from 7 percent in January. Seasonally adjusted employment added 20,400 new positions after adding 63,700 in January. Full time jobs declined by 22,800 but 43,300 part time positions were added. The participation rate, which measures the number of people in work or looking for jobs as a percentage of the population, fell to 63.9 percent from 64.1 percent in January.


Last Week's Highlights • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
|