
Indicator scoreboard
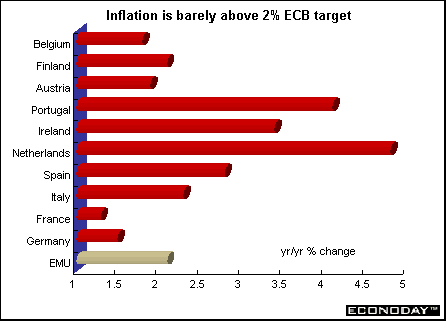
EMU - November harmonized index of consumer prices fell 0.1 percent but rose 2.1 percent when compared with last year. The decline was led by energy prices, down 1.5 percent from October, with help from transportation, hotels and restaurants, food, and communication costs. Core inflation excluding energy, food, alcohol and tobacco rose 0.1 percent and 2.2 percent on the year. The ECB's inflation ceiling is 2.0 percent.
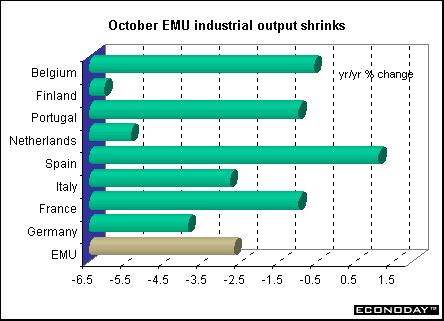
October seasonally adjusted industrial output dropped 1.4 percent and was 2.7 percent lower on the year. Output fell in all sectors led by a 1.9 percent decline in durable consumer goods, followed by energy goods and intermediate goods, both down 0.9 percent, capital goods down 0.8 percent and non-durable consumer goods down 0.7 percent. When compared with last year, durable consumer goods were down 6.9 percent, intermediate goods down 3.9 percent, capital goods down 2.3 percent, energy goods down 1.2 percent and non-durable consumer goods down 0.6 percent.
October seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus was E5.4 billion, down from the E5.8 billion surplus recorded in September. Both exports and imports fell 1.0 percent on the month. October trade surplus with the rest of the world was E7.6 billion - four times the surplus of E1.9 billion a year earlier. Exports fell an unadjusted 2 percent while imports fell 10 percent from October 2000 levels.
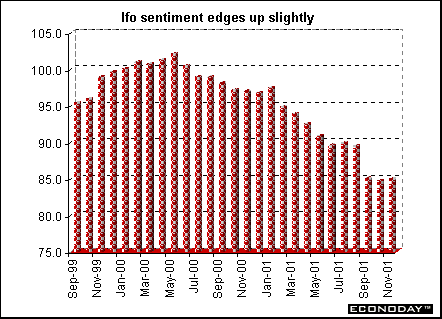
Germany - November Ifo Institute's west German business sentiment index rose slightly to 84.9 from 84.7 in October. It was the first increase since July. Ifo business expectations index rose for the first time since August, to 90.9 after an 89.6 reading in October. Current conditions, however, posted a drop to 79.1 from 79.9 in October.
France - October seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus widened to E1.950 billion. Imports dropped 6.5 percent led by semi-finished goods and machines, while auto and pharmaceuticals imports declined less. The energy deficit narrowed by 5.2 percent as oil prices fell. Exports declined 1.3 percent with semi-finished goods imports leading the decline, but household durables and telephone exports were also lower on the month. This was partly offset by auto, pharmaceuticals and aerospace exports.
November consumer spending on manufactured goods rose 0.2 percent and 2.8 percent when compared with last year. Spending rose, thanks to lower food and energy prices and retail discounts. Spending of cash reserves ahead of the changeover to the euro may have contributed as well.
Italy - November merchandise trade surplus with non-EU countries was 4.215 trillion lire, compared with a surplus of L88 billion a year ago. Non-EU exports rose 6.0 percent while imports sank 14.4 percent when compared with last year. The October trade balance with other EU countries worsened to a deficit of L255 billion compared with a surplus of L207 billion a year ago. Exports to other EU countries fell 3.0 percent on the year, while imports declined a more modest 1.1 percent.
October industrial orders fell 5.9 percent when compared with last year. Domestic orders fell 5.1 percent while foreign orders sank 7.1 percent. Domestic orders account for around 62 percent of the overall index. Industrial orders have posted eight consecutive declines. Industrial orders declined in eight of the ten product sectors. Recently introduced seasonally adjusted orders data showed October's orders fell 0.1 percent on the month. Domestic orders fell 0.8 percent while foreign orders rose 1.1 percent.
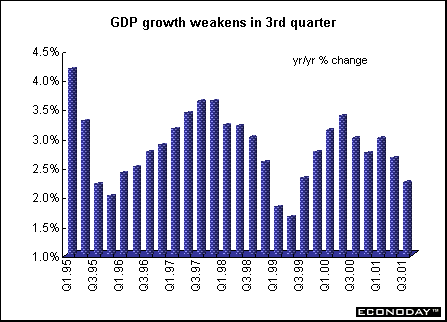
Third quarter seasonally adjusted gross domestic product rose 0.2 percent and 1.9 percent when compared with last year. Growth was due entirely to inventory accumulation. Growth in the third quarter was also helped by two more working days than in the second quarter (there were the same number of working days as in the third quarter of 2000). The GDP data are unique among large EMU countries in that they are seasonally but not workday adjusted.
November seasonally adjusted producer prices fell 0.2 percent but crept up 0.1 percent when compared with last year. Not seasonally adjusted producer prices fell 0.3 percent but rose 0.1 percent on the year. Excluding oil product prices, PPI was down 0.2 percent but also rose 0.1 percent on the year. Producer prices for semi-finished goods - which account for 31 percent of the PPI -fell 0.1 percent and 1.1 when compared with last year. Consumer goods fell 0.2 percent but rose 2.2 percent on the year. Consumer goods account for about 27 percent of the index, capital goods about 22 percent and energy goods 20 percent.
Britain - November merchandise trade deficit with countries outside the European Union widened to Stg2.047 billion from a deficit of Stg1.689 billion in October. Exports fell 6.6 percent while imports declined 1.2 percent. The drop in exports was widespread. The non-EU trade deficit excluding oil and erratics widened to Stg1.412 billion from Stg1.079 billion in October. The October EU trade gap widened to Stg625 million from Stg497 million in September, contributing to the widening of the world goods trade deficit in October to Stg2.314 billion from Stg2.253 billion in September.
Third quarter gross domestic product was up 0.5 percent and 2.2 percent when compared with last year. Government expenditure rose 0.7 percent on the quarter and 2.4 percent on the year. Household expenditure was up 1.1 percent and 4.0 percent on the year.
Asia
Hong Kong - Seasonally adjusted unemployment rate for the three months to November climbed to 5.8 percent from 5.5 percent in the August-to-October period. The increase in unemployment was widespread, led by job losses at manufacturers, builders, transportation companies and financial services providers.
Japan - October seasonally adjusted tertiary industry index, which tracks business at service providers, fell 0.4 percent. Restaurants and bars posted a record decline with a fall of 5.2 percent. The all-industry index, which adds industrial production and government spending to the services index, fell 0.5 percent in October after slipping 0.9 percent in September. The index, used as a proxy for gross domestic product, has fallen four straight months, the longest decline ever. When compared with last year, the tertiary index rose 0.2 percent and the all-industry index fell 3.1 percent.
Americas
Canada - October manufacturers' shipments declined 2.9 percent to the lowest level since May 1999. Temporary plant closures in the motor vehicle industry, slowing production in the aerospace sector, and declining petroleum and coal products prices held down shipments for a second consecutive month. When compared with last year, shipments fell 11.3 percent. Thirteen of 21 industries representing 62 percent of total shipments reported lower shipment values. Unfilled orders dropped 1.8 percent. Excluding aerospace products and parts industry, unfilled orders declined 0.9 percent. New orders dropped 5.1 percent to the lowest level since early 1999. Excluding aerospace products and parts industry, new orders were down 3.0 percent.
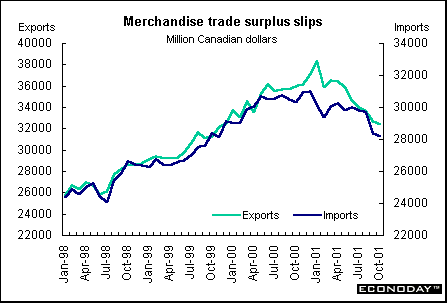
October merchandise trade surplus fell to C$4.2 billion. Both imports and exports fell to their lowest levels since November 1999. Exports were down 1.0 and imports down 0.6 percent. Exports fell for the seventh straight month and imports for the fourth consecutive month. Exports to the United States declined 1.6 percent and imports were down 0.6 percent. The trade surplus with the U.S. fell from C$7.5 billion to C$7.2 billion.
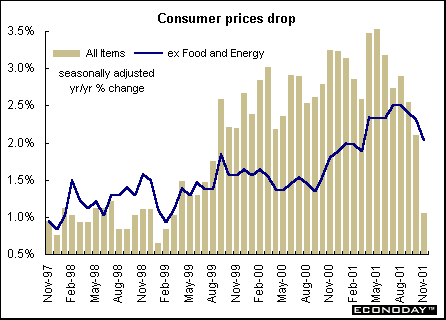
November unadjusted consumer prices were down 0.9 percent, the largest monthly decline since June 1959. When compared with last year, the CPI rose 0.7 percent. The decline was due mostly to weaker prices for gasoline, natural gas and traveler accommodations. Gasoline prices tumbled 10.0 percent following an 8.0 percent drop in the previous month. Natural gas prices fell 22.4 percent, the fifth consecutive monthly decline. Traveler accommodation fell 9.8 percent. The CPI excluding food and energy was down 0.2 percent but up 1.7 percent on the year. Seasonally adjusted CPI was up 1.1 percent while core CPI, excluding food and energy was up 2.0 percent on the year.
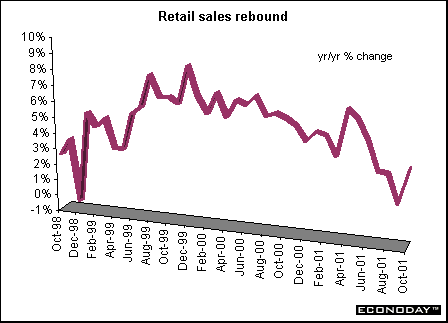
October retail sales rose 1.7 percent reversing the 1.5 percent decline in September. The recovery left sales essentially flat since April. About half of the October increase reflects stronger sales by motor and recreational vehicle dealers. Excluding them, retail sales climbed 1.1 percent after a 1.0 percent decline in September. In constant dollars, total retail sales rose 2.3 percent in October after falling 2.1 percent in September. Falling gasoline prices affected retail sales, with pump prices sinking 8.0 percent.


Introduction • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
|