
Indicator scoreboard
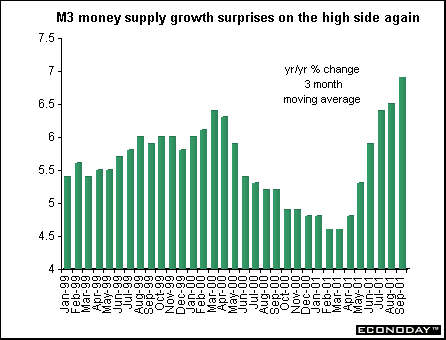
EMU - September M3 money supply growth rate jumped to 7.6 percent when compared with last year, up from an unrevised 6.7 percent in August. Three month moving average to September rose 6.9 percent when compared with the same three months last year. The ECB's target rate of M3 growth is 4.5 percent. The ECB said that the increase in M3 was associated with investor preference for liquidity in reaction to the increased uncertainty following September 11. The ECB estimated that foreign holdings of money market paper and debt securities with a maturity of less than two years - which have risen sharply due to investor uncertainty - might have distorted M3 growth upwards by about 75 basis points.
Germany - September seasonally adjusted import prices fell 0.8 percent and 3.6 percent when compared with last year. September seasonally adjusted export prices declined 0.1 percent and 0.3 percent on the year. Import prices have fallen continuously since June because of declining oil prices and the appreciation of the euro.
August seasonally adjusted industrial production rose a revised 2.2 percent from the 2 percent originally reported. The upward revision was due largely to stronger results in the energy and construction sectors. Energy goods production was revised up sharply to 1.5 percent from a flat reading reported initially. Output in the construction sector was also revised up strongly to 1.6 percent increase from the 0.9 percent originally reported. West German production was revised to 2.0 percent increase while in the east it was revised to 4.7 percent.
September producer prices rose 0.1 percent and 1.9 percent when compared with last year. The increase was caused by higher oil product prices, which rose 4.0 percent on the month. Excluding oil products, producer prices fell 0.1 percent but were up 2.6 percent on the year. Seasonally adjusted PPI was unchanged but up 1.9 percent when compared with last year.
France - September consumer spending on manufactured goods rose 0.2 percent and 5.1 percent when compared with last year. This was the fourth-straight monthly rise. Spending gains were led by a 2.2 percent increase for clothes, flanked by a 0.4 percent rebound in household durables and a further 0.5 percent rise in auto sales. Household spending excluding the auto sector (and medical products) was up 0.3 percent on the month and 3.5 percent higher on the year.
Italy - August unadjusted industrial orders fell 3.7 percent on the year after a 0.2 percent decline in July. Domestic orders rose 1.6 percent but foreign orders fell 9.8 percent as Italian manufacturing continued to suffer from the effects of the global slowdown. Domestic orders account for around 62 percent of the overall index, with foreign orders making up about 37 percent. Industrial orders rose in three out of 10 product sectors. Recently introduced seasonally adjusted monthly orders data, which are not closely followed by most analysts, showed August's orders rising 6.1 percent from July, the highest reading since December 2000. Domestic orders climbed 10.1 percent on the month, while orders from abroad were up 0.1 percent.
September merchandise trade surplus with non-EU countries was 9 billion lire. Non-EU imports fell 15.2 percent when compared with last year while exports were down 11.4 percent. The August merchandise trade deficit with its EU partners improved to L276 bln, compared with a deficit of L463 bln in August 2000. In August this year, EU exports fell 5.7 percent while imports were down 6.6 percent.
August unadjusted retail sales rose 0.4 percent and 3.0 percent on the year. All of the 15 product categories in the index rose. The strongest increases were pharmaceutical products, up 4.6 percent, and toys, up 4.5 percent. Food sales, which account for about 80 percent of the total index, rose 3.7 percent, while non-food sales climbed 2.5 percent.
Britain - The October Confederation of British Industry quarterly industrial trends survey showed that business confidence plunged to its lowest level in over three years. The survey was taken after September 11. Business optimism balance plunged to minus 54 percent from minus 22 in July. Optimism over export prospects fell at its fastest rate since July 1980, hitting minus 53 percent from minus 25 percent in July.
Third quarter gross domestic product rose 0.6 percent and 2.2 percent when compared with last year. Economic growth accelerated back up to its trend rate thanks to a buoyant retail sector and despite the global slowdown in economic activity. Service sector output was the driving force behind growth, up 0.8 percent and 3.5 percent on the year. The main impetus behind growth was a 1.3 percent quarterly gain in output of the distribution, hotels and catering industries. Within the industrial sector, output of the manufacturing industries is estimated to have fallen slightly on the quarter, partly due to a fall in output in the high-tech industries. Precise figures are not available with the first estimate.
Belgium - September Belgian National Bank's industry sentiment index dropped 4.9 points to minus 17.0, the lowest level since December 1995. After the plunge in the Ifo west German business sentiment index last week, the BNB survey gives further evidence of a dramatic deterioration in confidence that is likely dampen investment and hiring. The manufacturing component, widely seen as a leading cyclical indicator for the eurozone economy as a whole, plummeted 5.7 points as a growing majority of industry executives expect orders to decline sharply and prices to soften further in coming months.
Asia
Japan - September seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus rose to 724.9 billion yen from 632.9 billion yen in August. Imports fell 8.2 percent as manufacturers slowed production to reduce inventories built up by the drop in exports, which fell 4.6 percent. Export volumes to the United States, which accounts for 30 percent of Japan's trade, fell 18 percent from a year ago. Total export volumes dropped 14 percent and import volumes fell 9.7 percent from a year ago.
The tertiary industry index, which tracks retail, communications and other service industries, fell 0.1 percent, seasonally adjusted, in August after a 1 percent drop in July. The all-industry index, which tallies the production of all goods and services, fell 0.2 percent from a month ago, its second straight decline.
October consumer prices in Tokyo excluding fresh food were unchanged this month but were one percent lower than a year ago, the 25th straight drop from year earlier levels. September nationwide CPI dropped 0.8 percent when compared with last year. Those prices have not risen from year earlier levels since April 1998.
Americas
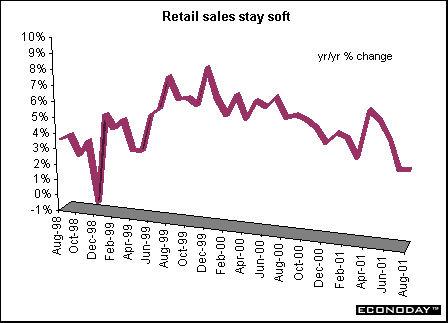
Canada - August retail sales rose 0.3 percent and 3.6 percent when compared with last year. Excluding motor and recreational vehicles dealers' sales, retail sales rose 0.5 percent and 4.6 percent when compared with last year. Retail sales have held relatively steady since April, however, sales by auto dealers, furniture stores and clothing stores have softened in recent months, which may indicate consumers cutting back on discretionary purchases.


Introduction • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
|