
Indicator Scoreboard
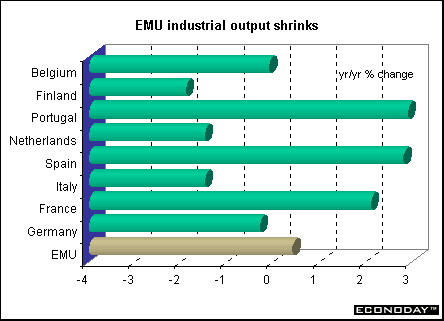
EMU - August industrial output rose 1.1 percent and 0.4 percent when compared with last year. Output rose in most sectors with durable consumer goods up 3.1 percent, followed by capital goods up 2.2 percent, intermediate goods up 0.5 percent and non-durable consumer goods up 0.3 percent. However, energy goods fell 0.3 percent. When compared with last year, capital goods rose 2.4 percent, energy goods rose 1.8 percent, non-durable consumer goods rose 1.6 percent and durable consumer goods rose 0.7 percent.
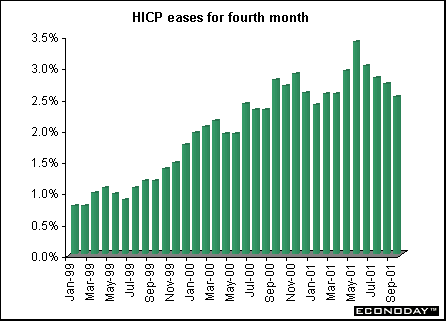
September harmonized index of consumer prices rose 0.3 percent and 2.5 percent when compared with last year. Core HICP excluding energy, food, alcohol and tobacco rose 0.1 percent and 2.2 percent on the year. Prices increased in September in nearly all categories led by a 2.1 percent increase in clothing and 1.2 percent rise in education. The annual HICP rate fell in seven out of 12 countries, rose in three and was unchanged in two.
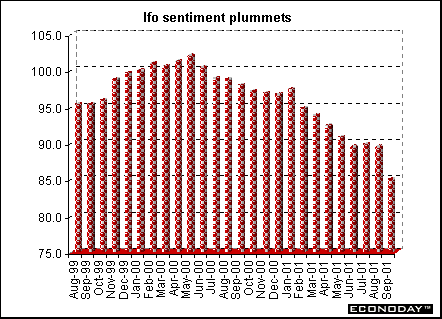
Germany - September Ifo Institute's west German business sentiment index sank to 85 from 89.5 in August. The index was at its the lowest point in nearly eight years (November 1993). Both business expectations and current conditions posted large declines, with expectations down to 90.6 from 95.9 in August and current conditions down to 79.6 from 83.2 the month before. All responses to the September Ifo survey were given after the September 11 attacks on the United States.
September wholesale price index rose 0.1 percent due to higher seasonal food and energy prices. However, when compared to last year, the WPI was down 0.2 percent, the lowest rate since July 1999. Excluding seasonal food prices, wholesale prices fell 0.1 percent on the month and 0.8 percent on the year. Many analysts view WPI cautiously, given the high weighting of oil products in the index, and say the Producer Price Index, due out this week, gives a better picture of the German inflation situation.
France - September preliminary seasonally and workday adjusted large store real sales fell 1.5 percent more than erasing the 0.9 percent recovery in August. Department stores sales dropped 3.4 percent, due largely to a decline in tourist spending in Paris stores after the terrorist attacks. Supermarket and hypermarket sales fell 0.3 percent and 0.4 percent, respectively.
July/August seasonally and workday adjusted manufacturing output rose 0.5 percent and 1.6 percent when compared with last year. Auto output was up 1.3 percent and consumer goods were up 0.6 percent. Semi-finished goods output rose 0.4 percent, while capital goods fell back 0.2 percent.
August seasonally adjusted merchandise trade surplus widened to E2.135 billion. Exports rose 11.1 percent thanks to the continued strength of auto and aircraft exports and the sale of an ocean liner for E464 million. Imports rose 2.9 percent led by a sharp rise in pharmaceutical imports from the U.S.
Italy - August seasonally and workday adjusted industrial production rose 0.6 percent but fell 1.5 percent when compared with last year. Not too much significance should be attached to August output data because it is notoriously volatile and strongly influenced by calendar effects connected to the timing of the summer holidays.
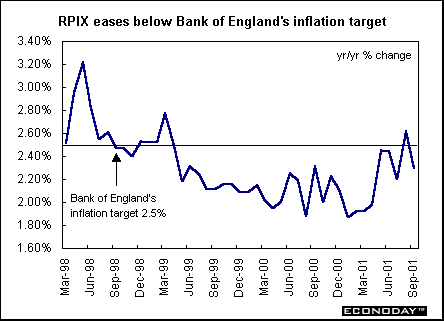
Britain - September retail price index rose 0.3 percent and 1.7 percent when compared with last year. The retail price index excluding mortgage interest payments rose 0.5 percent and 2.3 percent when compared with last year. The Bank of England uses the RPIX as their inflation measure. A decline in the price of gasoline helped drive the key RPIX inflation measure below the government's 2.5 percent.
September retail sales rose 0.2 percent down from August's revised 0.7 percent and slower than the 0.4 The survey was conducted from August 29 to September 29, so more than half was done after September 11. When compared with last year, retail sales rose 5.9 percent.
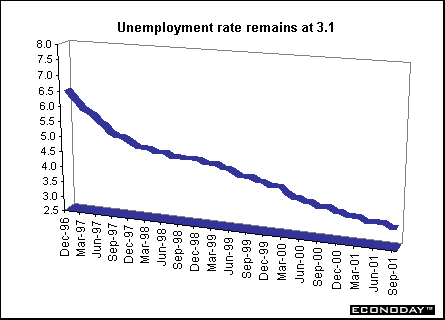
September claimant count unemployment rate remained unchanged at 3.1 percent. However, unemployment measured by International Labor Force methods rose 53,000 in the three months through August to 1.51 million from the previous three months. That unemployment rate rose to 5.1 percent from 4.9 in the three months through July.
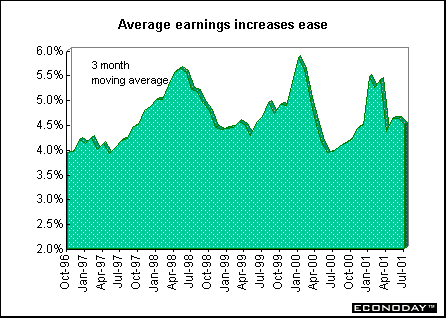
Average earnings growth slowed to 4.5 percent in the three months to August when compared with last year. Service sector earnings rose 3.8 percent, down from 4.0 percent in the previous period. Public sector earnings rose 5.7 percent.
August merchandise trade deficit widened to 3.3 billion pound from 2.5 billion pounds in July. Imports rose 2.3 percent while exports fell 2.8 percent. The September trade deficit with countries outside the EU shrank to 1.7 billion pounds from 3 billion pounds in August, the smallest monthly deficit since March 2000. In September, imports from countries outside the EU fell 13 percent while exports rose 1.2 percent.
Asia
Japan - September bankruptcies rose 0.4 percent when compared with last year. Bankruptcies among construction companies fell 4.3 percent from a year earlier, to 532.
Americas
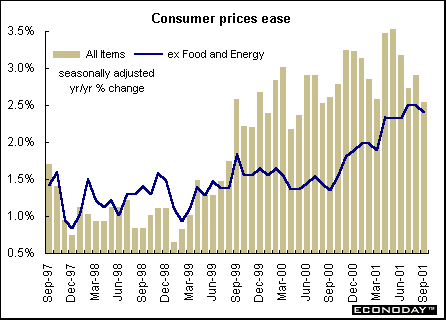
Canada - September consumer price index rose 0.3 percent and 2.6 percent when compared with last year. Rising gasoline prices were the main factor behind that monthly increase, but nearly 30 percent of the 12-month advance came from higher food prices. September CPI less food and energy rose 0.1 percent and 2.1 percent when compared with last year. Seasonally adjusted CPI rose 2.5 percent and core seasonally adjusted CPI rose 2.4 percent.
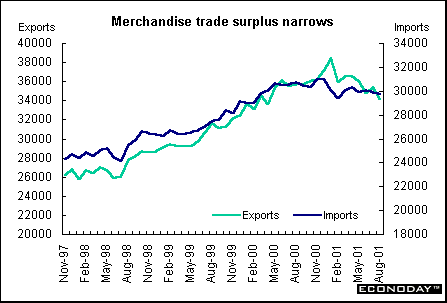
August merchandise trade surplus fell to C$4.43 billion. Exports fell 3.4 percent, their lowest level in 17 months with declines in all major commodity groups except automotive products. Imports fell 0.9 percent when increases in the automotive, agriculture and consumer goods sectors failed to offset larger declines in all other sectors. Merchandise exports to the United States declined 2.7 percent while imports were down 2.4 percent to C$21.4 billion, yielding a surplus that declined to C$8.03 billion from C$8.32 billion in July.
August manufacturing shipments rose 0.7 percent. Fourteen of 21 industries, representing 56 percent of total shipments increased. Price influences in the petroleum and coal products industry and in the food industry contributed to August's increase. Higher shipments were partly offset by declines in the computer and electronic products and motor vehicle parts industries. New orders decreased 0.6 percent. Lower orders in the aerospace product and parts industry were responsible. Aerospace products and parts manufacturers were primarily responsible for the decline. Excluding the impact of the aerospace industry, new orders climbed 1.7 percent. Unfilled orders, which have fluctuated throughout 2001, eased back 0.5 percent largely driven by the aerospace products and parts industry. Excluding the aerospace product and parts industry, unfilled orders rose 0.2 percent.
 |


Introduction • Global
Stock Market Indexes • Recap of Global Markets
• Currencies • Indicator
Scoreboard

The Bottom Line •
Looking Ahead
|